NPS are defined so the pipes can be simply interchangeable one with another. There is a number of standardized sizes and shapes for flanges and pipes.

Nominal pipe sizes define a pipe's outer diameter and flange inner diameter. This standardization is important because of pipe and flange interchangeability from various manufacturers. NPS is the single most important parameter of a pipe or a flange. By specifying the nominal pipe size which is a dimensionless number, most other actual dimensions of the flange follow from the standard. For example, ASME B16.5 Class 150, Size 8 instantly defines the flange outer diameter, thickness, and the mounting bolt pattern.
In other words, Nominal Pipe Size is a dimensionless number that indirectly relates to the pipe or flange physical size. The importance of having NPS in the industry is two-fold: it makes products interchangeable, and in a conveniently simple number NPS presents multiple actual dimensions of a flange.
DN stands for Diameter Nominal loosely spelled from the French "Diamètre Nominal". DN is the European equivalent of American NPS. In other words, for every NPS number there is a DN number; for example NPS 3/4" is equivalent to DN20. This means that a pipe having NPS 3/4" can also be defined as DN20, where 3/4 (0.75 inches) approximates the nearest standard size in millimeters which is DN20 since there is no DN19.05. Conversion from NPS to DN is straightforward, where the number in inches is converted to millimeters and the DN is the nearest standard size up or down. NPS 1/8 is DN6 because there is no DN less than DN6, NPS 1/4 is DN8 because DN6 is taken. The larger sizes make more sense where NPS 3/8 is DN10, with 9.525mm rounded up to 10mm which is standard DN10. And so on. There are plenty of NPT to DN conversion tables available from pipe and flange suppliers.
NPS and nominal flange size refer to the same dimensionless number. In other words nominal pipe size and nominal flange size is the same number, except NPS defines the pipe outside diameter, while nominal flange size defines the bore diameter of a flange. Think of a pipe and a flange being welded together. They will have the same nominal pipe size. Of note, blank flanges are also governed by the nominal flange sizes, where a bore can actually be machined in.
Shapes and sizes of vacuum flanges are not governed by any of the ASME standards. Typically vacuum flanges are measured in millimeter units, they fall under ISO dimensioning system. Vacuum flanges nominal sizes are, as in NPS in ASME flanges denote bore diameters, not the outer diameters, except for Conflat flanges, where a DN size indicates CF flange O.D.
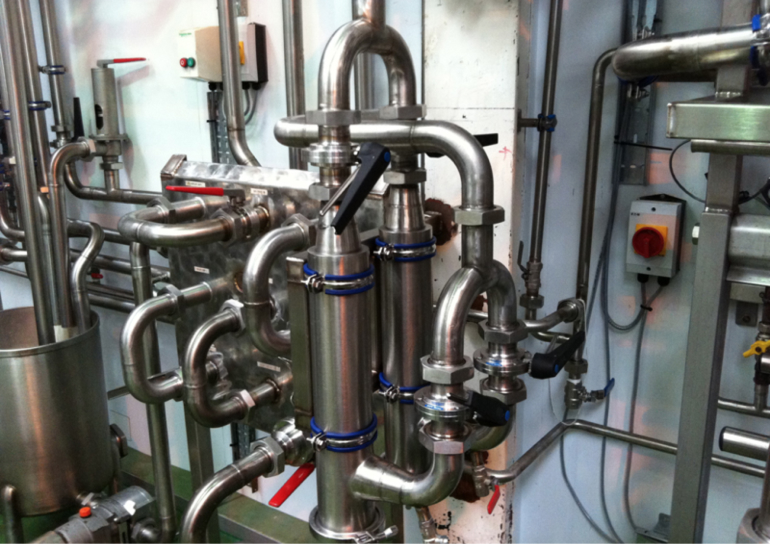
A relevant subject for pipe sizes is pipe threads. Pipes are connected together by welding or threding one into another. So, it's only fitting for this article to add this section on NPT threads. We use these charts when making NPT threads in our fittings and sight glasses.
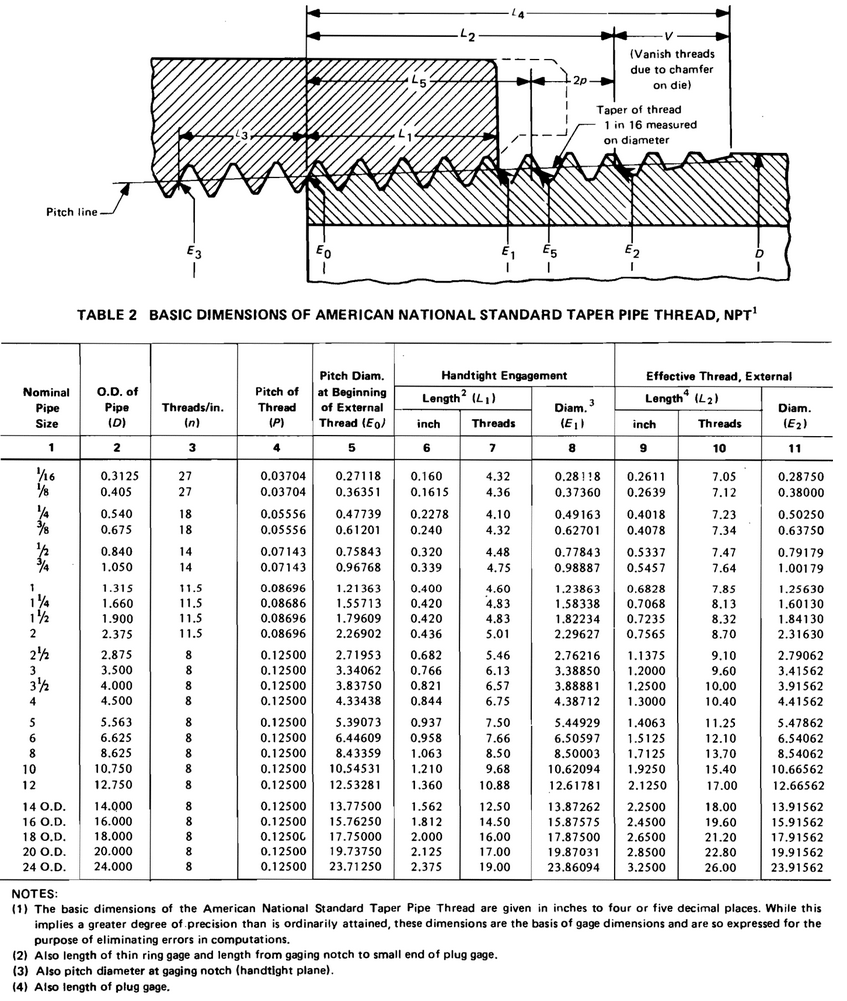
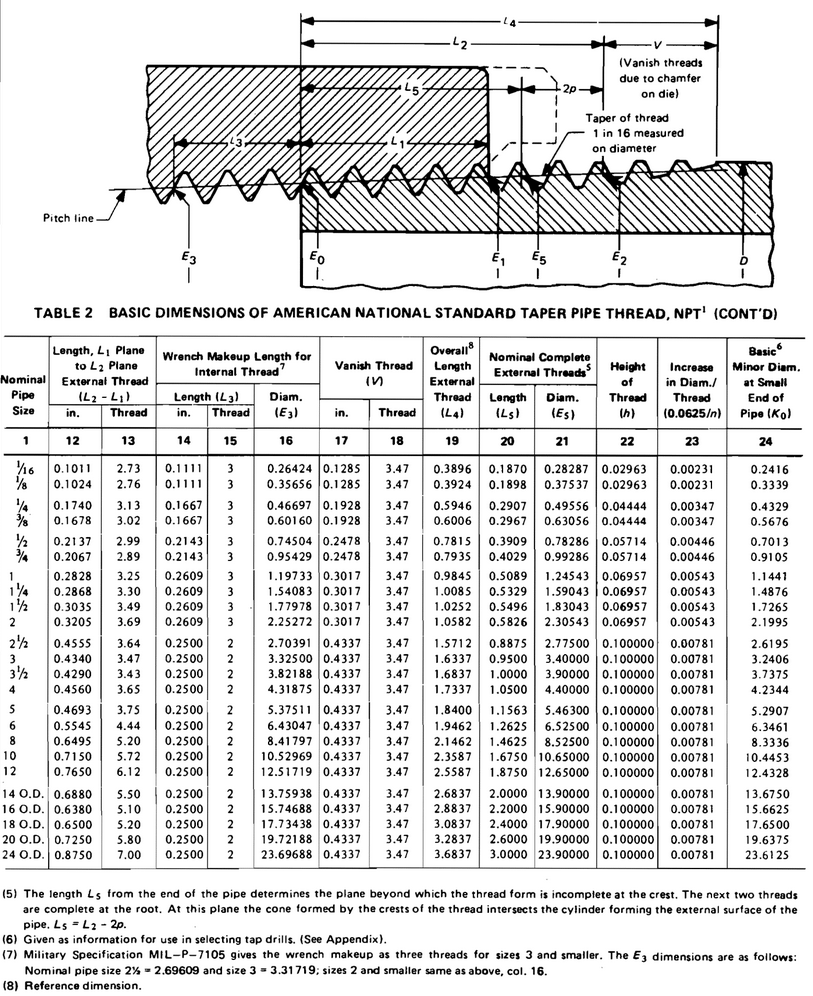
For internal threads, if using a reamer, your CNC operator can figure out the rest of the taper machined into the fitting. Use the target diameter from the table. Your product will fit and will pass the Go/No-Go gauge inspection. Here is a tutorial video on making NPT threads.